| CANCER |
Protective Dietary Components
-
Certain foods and nutrients have been shown to protect against certain types of cancers.
-
Vitamin C - has been shown to protect against cancer of stomach, esophagus, and oral cavity.
-
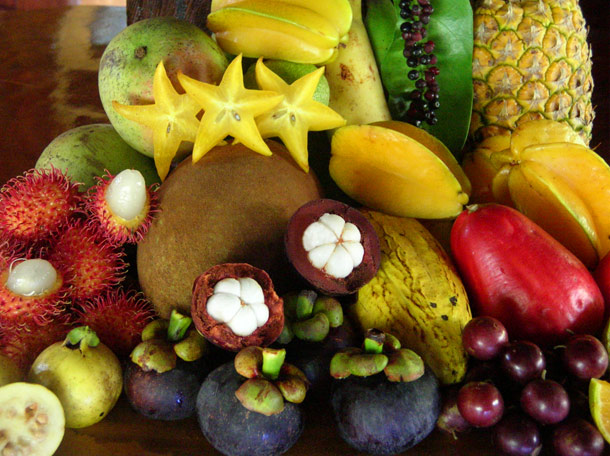
Antioxidants- these are certain nutrients found in fruits and vegetables.
-
Fruits and Vegetables- contain vitamins, fiber and phytochemicals.
-
Vitamin E and selenium- both antioxidants that protect cells against breakdown.
-
Calcium- Calcium reduces cell turnover rates.
-
Water- drinking more than 5 glasses a day, associated with a lower risk of cancer.
-
Fiber- Insoluble fiber is connected to decreased risk of colon cancer.
-
Beans, vegetables, whole grains and fruit are good sources.
-
Salt- some evidence links diets containing large amounts of foods preserved by pickling and salting to increased cancers of the stomach, nose and throat.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Diet and the Cancer Patient
-
Nutrition is an important part of treatment.
-
Eating the right kinds of food before, during and after treatment can help the patient feel better and stay stronger.
-
Treatments can have an affect on appetite.
-
People with cancer have unique nutrition needs.
-
Eating enough food is usually not a problem. Treatment can have an adverse effect on appetite.
-
Nutrition suggestions often emphasize eating high calorie, high protein foods.
-
Treatments kill cancer cells but they also kill healthy cells. This can cause side effects such as:
-
Loss of appetite, sore mouth or throat, dry mouth, dental and gum problems, changes in taste or smell, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue and depression.
-
It is very important to have good nutrition to minimize the side effects of cancer, prevent or reverse nutritional deficiencies, and to maximize the quality of life.
-
The best method of calorie intake is by mouth. Sometimes this is not possible.
-
Other options of intake are:
- Feeding Tube
- TPN or total parenteral nutrition- this is nutrition directly through a vein.
|
|




